JWT Tutorial
This tutorial demonstrates securing resources with JWT.
The example used in this tutorial is the end point:
- GET /resource to obtain the secured resource
WoOF configuration
The resource is configured with access restriction to prevent unauthorized access. The claims object may also be injected for more specific security logic.
public class SecuredResource {
@HttpAccess(ifRole = "tutorial")
public void secure(Claims claims, ServerHttpConnection connection) throws IOException {
connection.getResponse().getEntityWriter().write("Hello " + claims.getId());
}
}
The JWT security is configured with the JwtHttpSecuritySource. The below is the configuration of the tutorial.
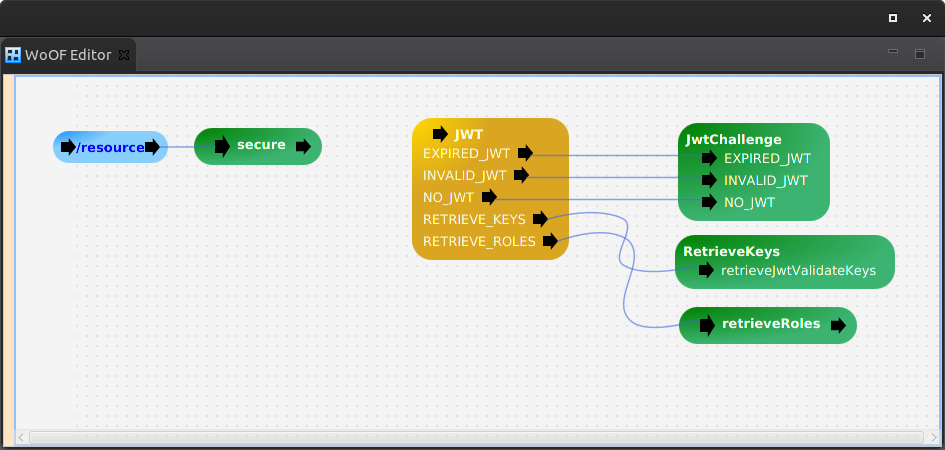
Many of the handlers for JWT are already available with default implementations:
- DefaultJwtChallengeSectionSource : for default JWT challenge handling
- JwksSectionSource : see JWKS below
These just need to be configured in as per this tutorial.
The claims is application specific so must be coded by the application. The tutorial claims is:
@Data
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Claims {
private String id;
private String[] roles;
}
The translation of JWT claims to roles is also very application specific. Therefore, it needs to be coded specifically for the application. The following is the example tutorial's translation of claims to roles:
public class JwtRoles {
public void retrieveRoles(@Parameter JwtRoleCollector<Claims> collector) {
collector.setRoles(Arrays.asList(collector.getClaims().getRoles()));
}
}
JWKS
RFC 7517 defines a format for publishing keys. The tutorial uses the default JwksSectionSource that adheres to this format to retrieve keys.
It, however, requires connecting to a server to retrieve JWKS content. The following is the mock implementation used by the tutorial. Production implementations would make HTTPS calls to the JWT Authority server to retrieve the keys.
public class MockJwksRetriever implements JwksRetriever {
@Override
public InputStream retrieveJwks() throws Exception {
// For production make HTTPS call to JWT Authority server to obtain JWKS content
// For tutorial, returning mocked JWKS response
RSAPublicKey key = (RSAPublicKey) Keys.keyPairFor(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256).getPublic();
JwksKeys keys = new JwksKeys(Arrays.asList(
new JwksKey("RSA", base64(key.getModulus()), base64(key.getPublicExponent()), 0, Long.MAX_VALUE)));
String content = mapper.writeValueAsString(keys);
return new ByteArrayInputStream(content.getBytes());
}
private static ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
private static String base64(BigInteger value) {
return Base64.getUrlEncoder().encodeToString(value.toByteArray());
}
@Data
public static class JwksKeys {
private final List<JwksKey> keys;
}
@Data
public static class JwksKey {
private final String kty;
private final String n;
private final String e;
private final long nbf;
private final long exp;
}
}
Testing
The following shows the ease of testing with JWT security:
public class JwtResourceHttpServerTest {
// Sets up server to accept created JWT access tokens for testing
@Order(1)
@RegisterExtension
public final MockJwtAccessTokenExtension authority = new MockJwtAccessTokenExtension();
@Order(2)
@RegisterExtension
public final MockWoofServerExtension server = new MockWoofServerExtension();
@Test
public void ensureResourceSecured() throws Exception {
MockHttpResponse response = this.server.send(MockHttpServer.mockRequest("/resource").secure(true));
response.assertResponse(401, "");
}
@Test
public void accessSecureResource() throws Exception {
// Create mock access token
String accessToken = this.authority.createAccessToken(new Claims("daniel", new String[] { "tutorial" }));
// Access the secured resource
MockHttpResponse response = this.server.send(
MockHttpServer.mockRequest("/resource").secure(true).header("authorization", "Bearer " + accessToken));
response.assertResponse(200, "Hello daniel");
}
}
JUnit 4 example:
public class JwtResourceHttpServerJUnit4Test {
// Sets up server to accept created JWT access tokens for testing
public final MockJwtAccessTokenRule authority = new MockJwtAccessTokenRule();
public final MockWoofServerRule server = new MockWoofServerRule();
@Rule
public final RuleChain orderedRules = RuleChain.outerRule(this.authority).around(this.server);
@Test
public void ensureResourceSecured() throws Exception {
MockHttpResponse response = this.server.send(MockHttpServer.mockRequest("/resource").secure(true));
response.assertResponse(401, "");
}
@Test
public void accessSecureResource() throws Exception {
// Create mock access token
String accessToken = this.authority.createAccessToken(new Claims("daniel", new String[] { "tutorial" }));
// Access the secured resource
MockHttpResponse response = this.server.send(
MockHttpServer.mockRequest("/resource").secure(true).header("authorization", "Bearer " + accessToken));
response.assertResponse(200, "Hello daniel");
}
}
Next
The next tutorial covers providing a JWT authority server.


